Eye melanoma
Eye melanoma, also called ocular melanoma, is the most common type of eye cancer.
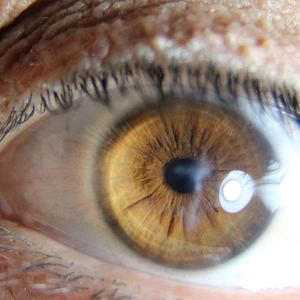
Melanoma is a type of cancer that develops in the cells that produce melanin (the pigment that gives your skin its colour). Because your eyes also have melanin-producing cells, they can develop melanoma.
Watery eyes symptoms
There are two types of eye melanoma:
- uveal melanoma – the most common type of eye melanoma that develops in the uvea, which sits beneath the white of the eyes
- conjunctival melanoma – a rarer type of eye melanoma that develops in the conjunctiva, a thin, clear membrane that lubricates and protects your eye
Eye melanoma does not typically cause early signs or symptoms, which can make it hard to identify. Individuals with a family history of melanoma, or excessive exposure to UV light may be at higher risk.
Uveal melanoma symptoms may include:
- blurred vision
- seeing a peripheral shadow
- experiencing flashing lights
In turn, conjunctival melanoma may manifest itself by:
- new brown or dark patches appearing on the white area or the surface of the eye
- existing brown or dark patches on the white area of the eye getting bigger
- a raised, skin-coloured bump on the white of the eye
When to see a consultant?
These symptoms can be caused by other eye conditions. However, if you have any of the signs or symptoms listed above, or you notice any sudden changes in your vision, you should make an appointment with a retinal specialist at The London Clinic Eye Centre.
You can request an appointment with one of the eye specialists from The London Clinic Eye Centre here.
* We offer fast appointments Monday - Friday only.